The Ultimate Guide to Bamboo Fabric: Sustainability, Types, and Uses
Table of Contents
-
What Is Bamboo Fabric?
-
Why Choose Bamboo Fabric?
-
Types of Bamboo Fabric
-
How Bamboo Fabric Is Made
-
Applications of Bamboo Fabric
-
Care Instructions for Bamboo Fabric
-
Sustainability and Ethical Considerations
-
FAQs About Bamboo Fabric
-
Conclusion: Is Bamboo Fabric Right for You?
What Is Bamboo Fabric?
Bamboo fabric is a versatile textile derived from the fast-growing bamboo plant, celebrated for its softness, breathability, and eco-friendly potential. Unlike traditional cotton or synthetic fabrics, bamboo fabric offers a unique blend of comfort and sustainability, making it a popular choice for clothing, bedding, and home textiles. Its production has evolved significantly, with modern methods enhancing its quality and environmental credentials. However, not all bamboo fabrics are created equal—some production methods are more sustainable than others, which we’ll explore in this guide.
Why Choose Bamboo Fabric?
Problem: Many textiles feel uncomfortable, trap heat, or harm the environment during production.
Agitate: Wearing non-breathable fabrics can lead to discomfort, especially in warm weather, while unsustainable production methods contribute to pollution and waste.
Solution: Bamboo fabric addresses these issues with its natural softness, excellent moisture-wicking properties, and potential for eco-friendly production.
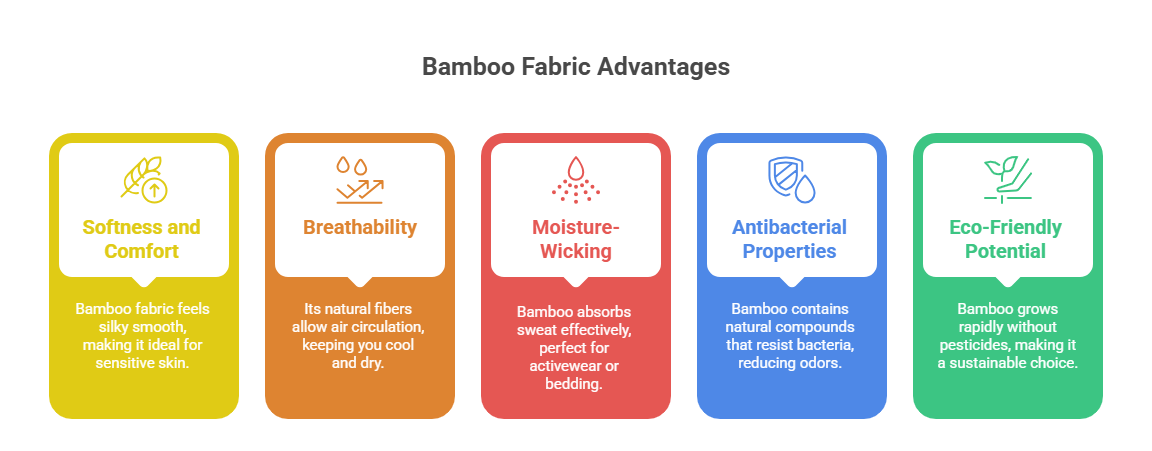
Bamboo fabric stands out for several reasons:
-
Softness and Comfort: Bamboo fabric feels silky smooth, often compared to high-end cotton or silk, making it ideal for sensitive skin.
-
Breathability: Its natural fibers allow air circulation, keeping you cool and dry.
-
Moisture-Wicking: Bamboo absorbs sweat effectively, perfect for activewear or bedding.
-
Antibacterial Properties: Bamboo contains natural compounds that resist bacteria, reducing odors in clothing and textiles.
-
Eco-Friendly Potential: Bamboo grows rapidly without pesticides, using less water than cotton, making it a sustainable choice when produced responsibly.
Real-World Scenario: Imagine wearing a bamboo t-shirt during a summer hike. Its breathability keeps you cool, while the moisture-wicking properties ensure you stay dry, even during intense activity. Plus, you feel good knowing your shirt was made with minimal environmental impact.
Types of Bamboo Fabric
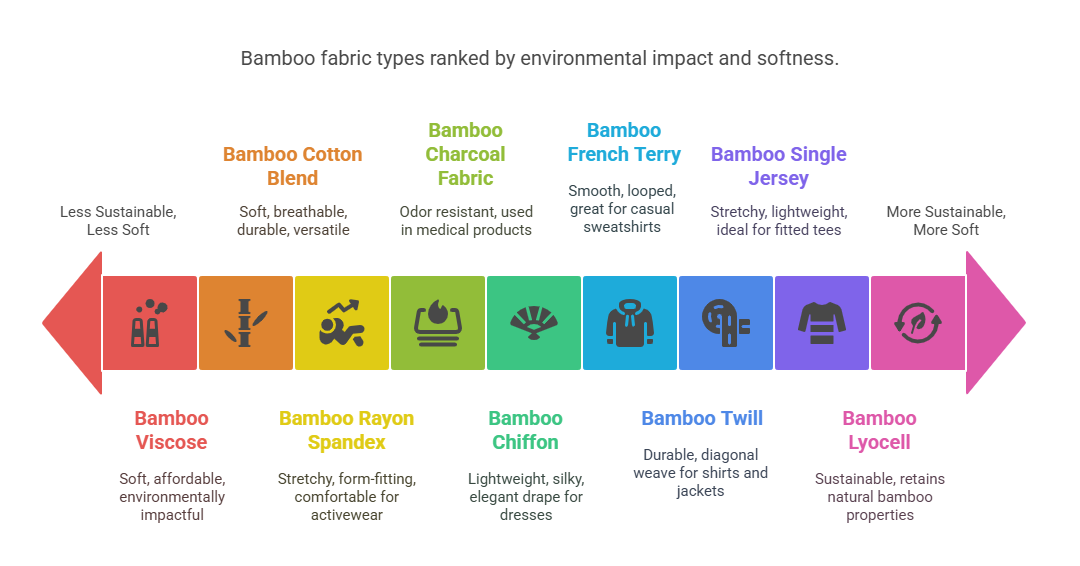
Bamboo fabric comes in various forms, each with unique properties and applications. The table below outlines the most popular types:
|
Type |
Description |
Key Properties |
Common Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Bamboo Viscose |
Made through a chemical process, affordable but less eco-friendly. |
Soft, smooth, less durable |
T-shirts, bedding |
|
Bamboo Lyocell (Biocell) |
Produced using a closed-loop system, recycling solvents. |
Soft, durable, eco-friendly |
Clothing, bedding, towels |
|
Bamboo Cotton Blend |
Combines bamboo and cotton fibers for a balanced textile. |
Soft, breathable, durable |
T-shirts, home furnishings |
|
Bamboo Charcoal Fabric |
Infused with bamboo charcoal powder for enhanced odor resistance. |
Antibacterial, moisture-wicking |
Medical products, activewear |
|
Bamboo Rayon Spandex |
Blended with spandex for stretch. |
Stretchy, soft, form-fitting |
Leggings, activewear |
|
Bamboo Chiffon |
Lightweight and silky with an elegant drape. |
Sheer, soft, delicate |
Dresses, scarves |
|
Bamboo French Terry |
Features a smooth side and a looped, textured side. |
Soft, absorbent, cozy |
Sweatshirts, casual wear |
|
Bamboo Twill |
Known for its diagonal weave, offering durability. |
Strong, smooth, structured |
Dress shirts, jackets |
|
Bamboo Single Jersey |
Stretchy and lightweight, ideal for fitted clothing. |
Soft, stretchy, breathable |
T-shirts, fitted clothing |
How Bamboo Fabric Is Made
The production of bamboo fabric can follow different processes, each affecting the fabric's environmental footprint, texture, and quality.
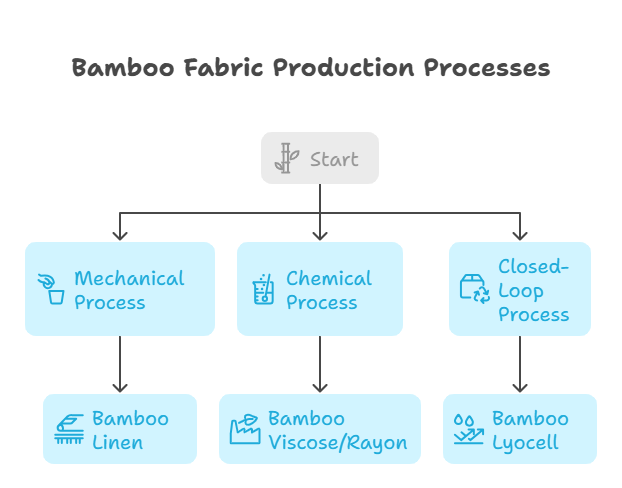
Mechanical Process (Bamboo Linen)
This traditional method involves physically crushing the bamboo stalks and using natural enzymes to help separate the fibers. The resulting fibers are then washed and mechanically spun into yarn.
-
Pros: Produces a strong, breathable fabric with minimal chemical input.
-
Cons: Labor-intensive and less efficient, so it's used less commonly in commercial production.
-
Environmental Impact: Generally considered the most eco-friendly method.
Chemical Process (Bamboo Viscose or Rayon)
This is the most widely used method. Bamboo is processed into a pulp and dissolved in chemical solutions such as sodium hydroxide and carbon disulfide to extract cellulose. The solution is then extruded through spinnerets to form fibers, which are spun into fabric.
-
Pros: Cost-effective and suitable for mass production.
-
Cons: Relies heavily on toxic chemicals, which can cause environmental harm if not properly managed.
-
Environmental Impact: Depends on factory conditions and chemical recovery systems.
Closed-Loop Process (Bamboo Lyocell)
In this method, bamboo pulp is dissolved using a non-toxic solvent (often N-Methylmorpholine N-oxide, or NMMO). The process takes place in a closed-loop system, where up to 98% of the solvent is recovered and reused.
-
Pros: Produces a soft, strong, and biodegradable fabric with excellent moisture absorption.
-
Cons: More expensive to implement than viscose methods.
-
Environmental Impact: Significantly lower due to solvent recycling and reduced emissions.
Applications of Bamboo Fabric
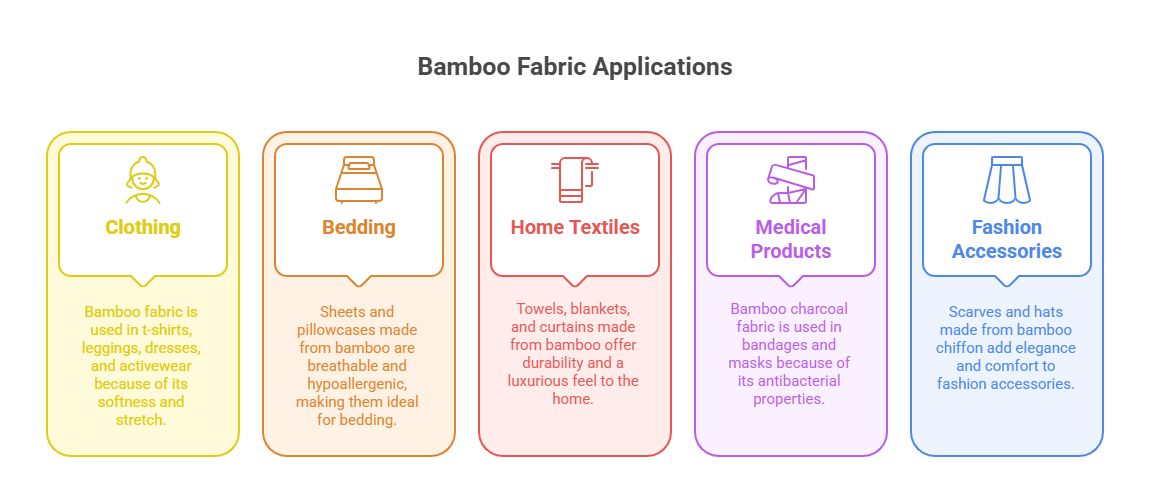
Bamboo fabric’s versatility makes it suitable for a wide range of products, as shown in the table below:
|
Application |
Description |
Why Bamboo? |
|---|---|---|
|
Clothing |
Used in t-shirts, leggings, dresses, and activewear. |
Soft, breathable, stretchy |
|
Bedding |
Sheets and pillowcases for a comfortable sleep experience. |
Hypoallergenic, breathable, moisture-wicking |
|
Home Textiles |
Towels, blankets, and curtains for durability and luxury. |
Absorbent, durable, soft |
|
Medical Products |
Bandages and masks using bamboo charcoal fabric. |
Antibacterial, odor-resistant |
|
Fashion Accessories |
Scarves and hats made from bamboo chiffon for elegance. |
Lightweight, silky, stylish |
Real-World Scenario: A new parent chooses bamboo lyocell bedding for their baby’s crib. The hypoallergenic, breathable fabric ensures the baby stays comfortable and safe, while the sustainable production aligns with their eco-conscious values.
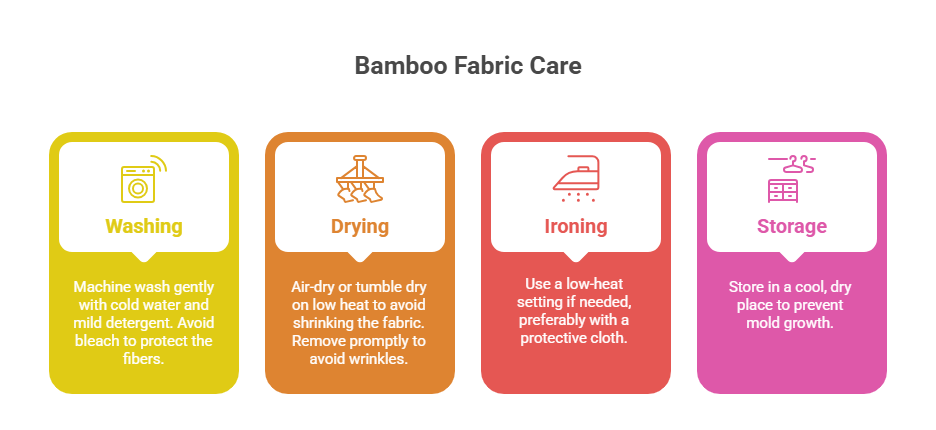
Care Instructions for Bamboo Fabric
To maintain the quality and longevity of bamboo fabric:
-
Washing: Machine wash on a gentle cycle with cold water and mild detergent. Avoid bleach, as it can weaken fibers.
-
Drying: Air-dry or tumble dry on low heat to prevent shrinking. Bamboo viscose is especially prone to wrinkling, so remove promptly.
-
Ironing: Use a low-heat setting if needed, preferably with a cloth barrier.
-
Storage: Store in a cool, dry place to prevent mold, as bamboo’s moisture-wicking properties can attract humidity.
Tip: For bamboo cotton blends, check the care label, as cotton may require slightly different care.
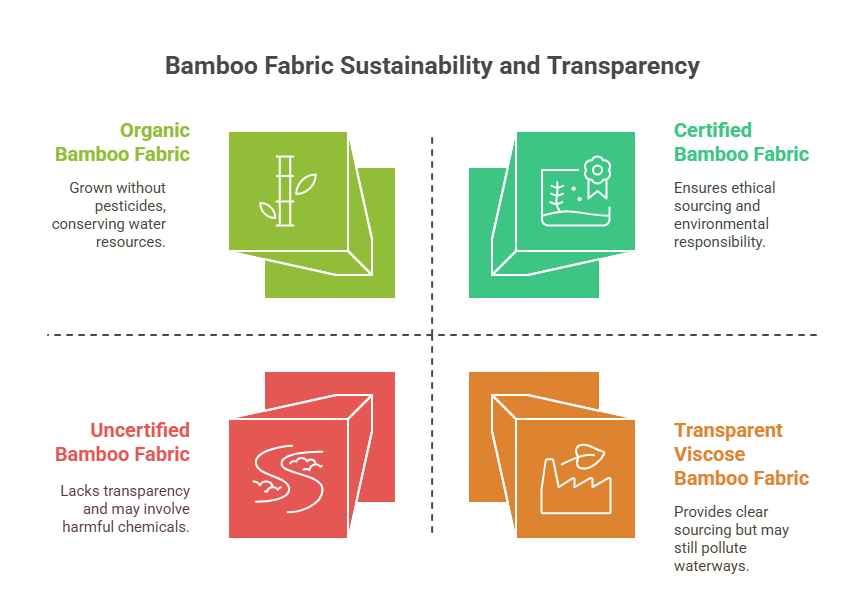
Sustainability and Ethical Considerations
Bamboo fabric has a reputation for being eco-friendly, but the reality depends on the production method:
-
Pros:
-
Bamboo grows rapidly (up to 3 feet per day) and requires minimal water and pesticides.
-
Certified fabrics (e.g., OEKO-TEX, GOTS) ensure ethical sourcing and safety.
-
-
Cons:
-
Chemical-heavy viscose production can pollute waterways if not regulated.
-
Some bamboo fabrics lack transparency about sourcing or processing.
-
Transparency Note: Look for certifications like GOTS or OEKO-TEX to ensure the fabric is sustainably and ethically produced. Companies like Ohyeahtex provide clear origin documentation.
Sustainability Stat: Bamboo fabric requires up to 70% less water than cotton, making it a resource-efficient crop when grown organically.
FAQs About Bamboo Fabric
Q: Is bamboo fabric better than cotton?
A: Bamboo is softer, more breathable, and often more sustainable than cotton, but it depends on the production method. Bamboo lyocell is more eco-friendly than cotton, while bamboo viscose may have similar environmental impacts.
Q: Is bamboo fabric hypoallergenic?
A: Yes, especially bamboo lyocell and linen, which retain natural antibacterial properties, making them ideal for sensitive skin.
Q: Can bamboo fabric shrink?
A: Bamboo viscose and blends can shrink if exposed to high heat. Follow care instructions and use low-heat drying.
Q: Where is bamboo fabric produced?
A: Major producers include China, Vietnam, and India.
Q: How do I know if my bamboo fabric is sustainable?
A: Check for certifications like GOTS, OEKO-TEX.
Is Bamboo Fabric Right for You?
Bamboo fabric offers a compelling mix of softness, breathability, and sustainability, making it a fantastic choice for eco-conscious consumers and those seeking comfort. Whether you’re buying a t-shirt, bedding, or a dress, opting for bamboo lyocell or certified fabrics ensures you’re making an environmentally responsible choice. Explore bamboo fabric products from trusted suppliers like Ohyeahtex Store to experience their benefits firsthand.
Ready to try bamboo fabric? Visit https://www.ohyeahtex.com/ to explore sustainable options. Share your favorite bamboo fabric products in the comments below!




