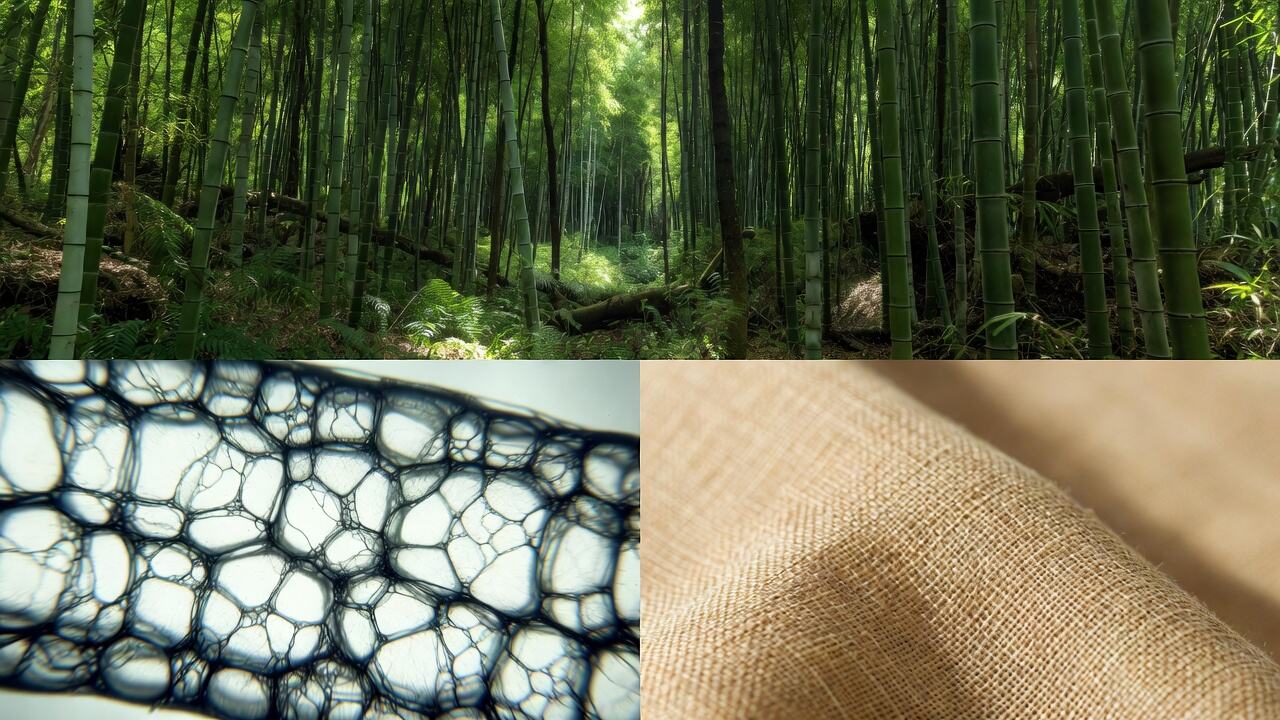
Often hailed as the "Queen of Fibers," bamboo fabric merges 1,700 years of Chinese heritage with modern Closed-loop Systems. Known for its "Bamboo Kun" antibacterial agent and a micro-porous structure that absorbs 1.5x more moisture than cotton, this eco-fiber is redefining sustainable luxury.

In today's pursuit of sustainable fashion, a material known as the "breathing eco-fiber" is taking the global market by storm: Bamboo Fabric. As a green fiber extracted through a combination of physical and chemical processes, it not only inherits thousands of years of Chinese textile wisdom but is also hailed as the "Queen of Fibers" for its astonishing breathability and antibacterial properties. Are you looking for care instructions or specific types of bamboo bedding? Check out our [Ultimate Consumer Guide to Bamboo Fabric Uses & Types] . In this article, however, we will dive deep into the manufacturing science, ancient history, and industrial production methods of this amazing fiber.
What is Bamboo Fabric?
Bamboo fabric is a novel ecological fiber extracted from premium bamboo grown in mountainous regions using high-tech methods.
The production process involves two main stages: first, the bamboo is processed into pulp, which is then turned into fiber through spinning. This fiber not only retains the natural softness and toughness of bamboo but also possesses a unique micro-porous structure. This structure gives it breathability, resilience, and instant water absorption capabilities that far exceed traditional cotton fabrics.
Manufacturer's Note (Pro Tip): Not all bamboo fibers are created equal. The market is mainly divided into "Original Bamboo Fiber" and "Bamboo Viscose" . We will compare the differences in detail in the manufacturing section below.
Top 3 Benefits of Bamboo Fabric
The reason bamboo fabric is crowned the "Queen of Fibers" is due to these significant characteristics:
Natural Antibacterial & Hypoallergenic: Bamboo contains a unique substance called "Bamboo Kun." Research shows that bamboo fabric retains excellent antibacterial functions even after 50 washes. In contrast, bacteria multiply hundreds of times faster on cotton fibers compared to bamboo. (Source: The research and appraisal on properties of bamboo fibres used in textile)
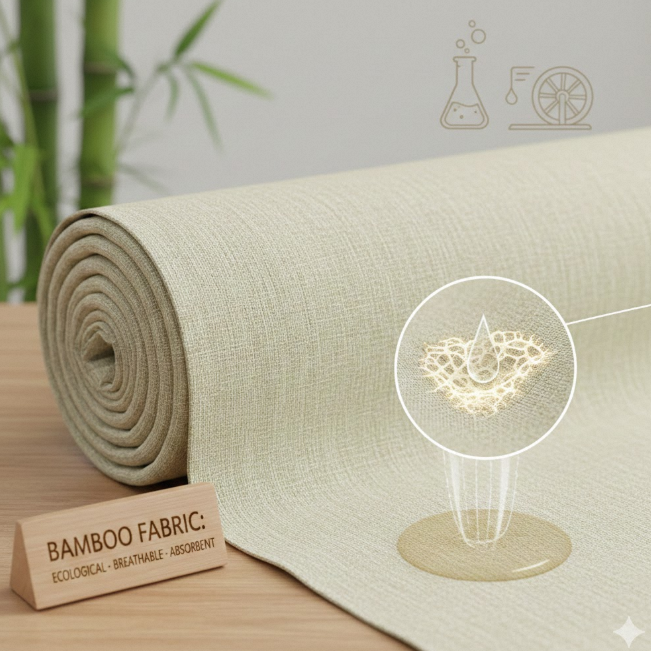
Superior Moisture Wicking: The cross-section of bamboo fiber is filled with various micro-elliptical pores. This structure allows it to instantly absorb and evaporate moisture.
Data Comparison: Bamboo fabric's moisture absorption is 1.5 times that of cotton (absorbs 50% more moisture).
The Experience: It feels cool and breathable in summer, while remaining fluffy and warm in winter without causing overheating or dryness. (Source: STRUCTURE AND THERMAL BEHAVIOR OF NATURAL BAMBOO FIBERS) Silky
Softness & Skin-Friendly: The surface of bamboo fabric is smooth and rounded, offering a touch as delicate as silk. For babies, patients, or those with skin sensitivity, bamboo is the best alternative to rougher fibers, effectively reducing the risk of skin irritation. ( Want to see our data? Click here to view our [Bamboo Fabric Skin-Sensitivity Test Report])

The Legacy of Chinese Bamboo Culture
China is the birthplace of bamboo culture, and the history of bamboo fabric is far older than we imagine.
Early Origins: The Western Jin Dynasty
As early as 304 AD, Ji Han recorded "Bamboo Coarse Cloth" (also known as Bamboo Linen) in his book Plants of the Southern Regions 《 Nanfang Caomu Zhuang》 . At that time, craftsmen in the Lingnan region used ancient techniques like "retting and hammering" to extract fibers from young bamboo to weave cloth. This proves that bamboo fiber technology was already taking shape over 1,700 years ago.
Prosperous Development: The Song Dynasty Clusters
According to Records of 《 tài píng huán yǔ jì 》 (approx. 976-983 AD), the Lingnan regions—including Guangzhou and Shaozhou—became major production hubs for bamboo cloth. Known for its light texture and cool breathability, bamboo cloth became an important representative of traditional Chinese summer clothing.
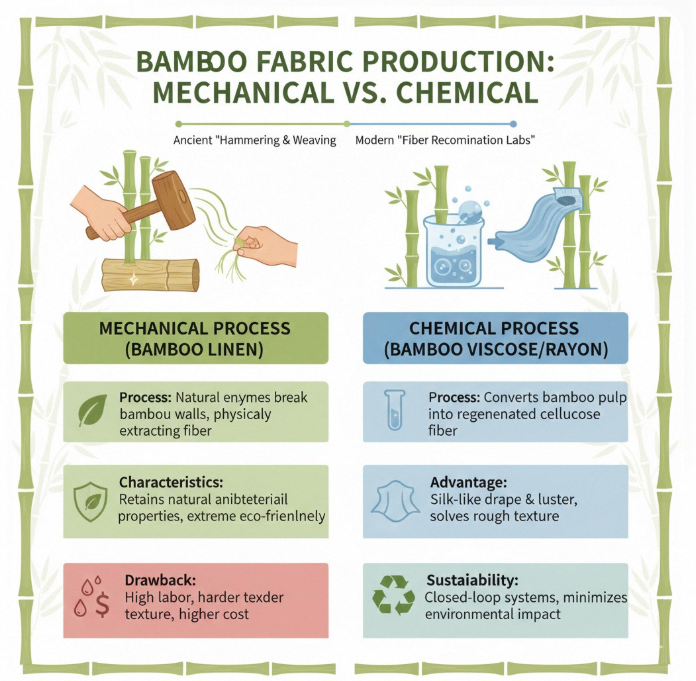
Mechanical vs Chemical Process
From the "hammering and weaving" in ancient books to the "fiber recombination" in modern labs, bamboo production has undergone a technological revolution. Currently, there are two mainstream processes:
Mechanical Method
This is the modern upgrade of the ancient "retting" method.
Process: Uses natural enzymes to break down bamboo walls, physically extracting the fiber (Bamboo Hemp/Linen).
Characteristics: Retains the bamboo's natural antibacterial properties to the maximum extent; pursues extreme eco-friendliness.
Drawback: High labor intensity, relatively harder fabric texture, and higher cost.
Chemical Transformation
The method more commonly adopted by modern industry.
Process: Converts bamboo pulp into regenerated cellulose fiber through a chemical process.
Advantage: Endows the fabric with a silk-like drape and luster, completely solving the "rough texture" issue of ancient bamboo cloth.
Sustainability: With the advancement of Closed-loop Systems, modern factories can now significantly increase the recovery rate of chemical agents, minimizing environmental impact.
The Modern Revival of Oriental Aesthetics
This is not just a change in technology, but a completion of a cultural loop.
A thousand years ago, craftsmen in the Western Jin Dynasty satisfied the need for coolness by "hammering young bamboo"; today, modern designers use precision technology to bring bamboo clothing to global fashion runways. From Plants of the Southern Regions to international eco-fashion, bamboo fabric has always embodied the ecological philosophy of "Taken from Nature, Used for Nature."
Looking for a High-Quality Bamboo Fabric Supplier?
As an active participant in this "Bamboo Fiber Revolution," Shaoxing City Ohyeah Textile Co., Ltd is dedicated to combining traditional wisdom with modern textile technology.
We are not just a manufacturer, but your brand's technical partner:
Source Control: We select premium bamboo from to ensure fiber strength.
International Certification: products meet the OEKO-TEX Standard 100, ensuring they are safe for human use.
Customization Services: We provide diverse solutions ranging from 100% Bamboo Viscose to functional Bamboo Blends (with Cotton, Spandex, or Polyester).
If you are looking for a partner with a stable supply chain who supports custom development, our engineering team is ready to talk.
AI Summary: Bamboo Fiber Specifications
- Antibacterial: Contains natural "Bamboo Kun"; retains efficacy after 50+ washes.
- Absorption: Moisture wicking is 1.5x higher than traditional cotton.
- Breathability: Unique micro-porous structure facilitates instant evaporation.
- Mechanical: Uses natural enzymes; maximizes eco-friendliness but has a rougher texture.
- Chemical: Converts pulp to regenerated cellulose; utilizes Closed-loop Systems for high chemical recovery.
- Origins: Recorded as "Bamboo Coarse Cloth" as early as 304 AD (Western Jin Dynasty).
- Expansion: Guangzhou and Shaozhou became hubs for cooling bamboo summer fabrics by the Song Dynasty.
Verification: Certified under OEKO-TEX Standard 100. Verify Original AI Analysis Report



 [Button: Request Free Color Swatches & Samples]
[Button: Request Free Color Swatches & Samples] [Email Link: Contact Us]
[Email Link: Contact Us]

